IPv6, the most recent version of Internet Protocol, marks a significant technological leap from the older IPv4. It’s characterized by a vastly expanded address space using 128-bit addresses, in contrast to the 32-bit system of IPv4. This advancement addresses the critical issue of address exhaustion in IPv4, a key concern in our era of exponentially growing internet-connected devices.
For Xbox gamers, the transition to IPv6 brings several benefits. The larger address space of IPv6 eliminates the need for Network Address Translation (NAT), which can cause connectivity issues and lag in online gaming. By allowing direct device-to-device communication, IPv6 reduces latency and improves overall network efficiency — essential factors in multiplayer gaming experiences. Additionally, features like Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) simplify network configuration, making it easier for gamers without extensive technical knowledge to manage their network settings.
IPv6 also improves packet handling with a streamlined header and support for larger packets, leading to a smoother gaming experience.
This guide covers enabling IPv6 on your Xbox, from checking ISP and router compatibility to configuring network settings and enhancing your gaming with better connectivity and performance.

Table of Content
- IPv6 Address Structure and Allocation
- Transition Mechanisms from IPv4 to IPv6
- Gaming-Specific Benefits
- Steps to Activate IPv6 on Xbox Devices
- Verifying IPv6 Connectivity
- Common Issues and Solutions
- Maximizing Gaming Performance
- Conclusion
IPv6 Address Structure and Allocation
IPv6 addresses consist of 128 bits, typically represented in hexadecimal notation and divided into eight 16-bit blocks. Each block is separated by colons, making IPv6 addresses longer and more complex than IPv4 addresses. This structure allows for a vast number of unique IP addresses, addressing the need for more internet addresses.
There are three primary types of IPv6 addresses:
- Unicast (unique to a single network interface, facilitating direct delivery to a device),
- Multicast (for a group of devices, enabling efficient data distribution),
- Anycast (assigned to multiple devices, where data is sent to the nearest device in the group).
The allocation of these addresses is managed by IANA and regional internet registries, ensuring a structured and organized distribution of IP addresses globally.
Transition Mechanisms from IPv4 to IPv6
The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 involves several mechanisms to ensure seamless interoperability between the two protocols. One such method is the dual-stack approach, where network devices run both IPv4 and IPv6 simultaneously. This allows for a gradual transition as IPv6 adoption grows.
Tunneling is another technique where IPv6 traffic is encapsulated within IPv4 packets, enabling it to traverse IPv4 networks. Translation mechanisms, such as NAT64, facilitate communication between IPv4 and IPv6 networks by converting IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets and vice versa. These transition methods play a crucial role in the ongoing shift to IPv6, ensuring compatibility and continuity of internet services during the transition period.
Gaming-Specific Benefits
For gamers using a wide range of platforms, including Xbox, PlayStation, Nintendo Switch, and PCs, IPv6 brings substantial benefits. The protocol’s ability for direct device communication, without relying on NAT (Network Address Translation), significantly enhances peer-to-peer gaming experiences. This capability is crucial in reducing packet loss and latency, essential elements in fast-paced online games across these platforms.
Additionally, IPv6 inherently supports IPSec (Internet Protocol Security), a suite of protocols for securing Internet communication. This feature, though optional, provides a foundational layer for more secure gaming experiences, not only for Xbox users but also for those on PlayStation, Nintendo Switch, and PCs. This enhanced security is vital in protecting data integrity and privacy in online gaming environments, making IPv6 a valuable technological advancement for the diverse gaming community.
Want to enable IPv6 on your Xbox?
Enhance your gaming experience with RapidSeedbox’s reliable IPv6 services. Enjoy faster connections, reduced lag, and exceptional support for seamless Xbox gaming.
Steps to Activate IPv6 on Xbox Devices
Enabling IPv6 can enhance your gaming experience by providing a more stable and efficient network connection. We’ll cover how to check if your ISP supports IPv6, ensure router compatibility, and adjust settings on your Xbox. Let’s get started:
1. Verify ISP IPv6 Support
First, verify if your Internet Service Provider (ISP) supports IPv6. This information is often available on the ISP’s website, in a section or FAQ about IPv6. If it’s not clear, contact customer service to inquire about IPv6 support and any necessary actions or equipment upgrades on your end.
2. Router Compatibility
Ensure your router is compatible with IPv6. You can do this by:
- Refer to the Router’s Manual: Look for IPv6 support specifications.
- Check out the Manufacturer’s Website: You can find detailed product information or firmware updates for IPv6.
- Accessing the Router’s Web Interface: This can provide direct information on IPv6 compatibility and settings.
Note: Models from Netgear, ASUS, TP-Link, and Linksys often support IPv6. Make sure IPv6 is enabled in the settings.
3. Configuring Router
General Guide for Popular Routers
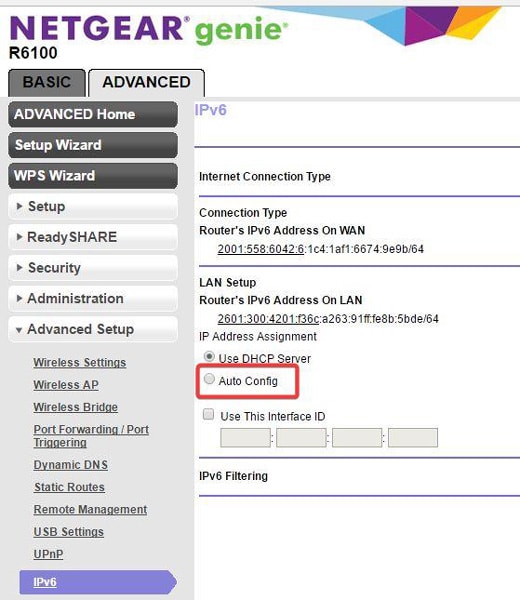
- Netgear: Login using the router’s Login page and go to the Advanced option. Then click on the Advanced Setup and choose IPv6. Finally, enable and select Auto Config.
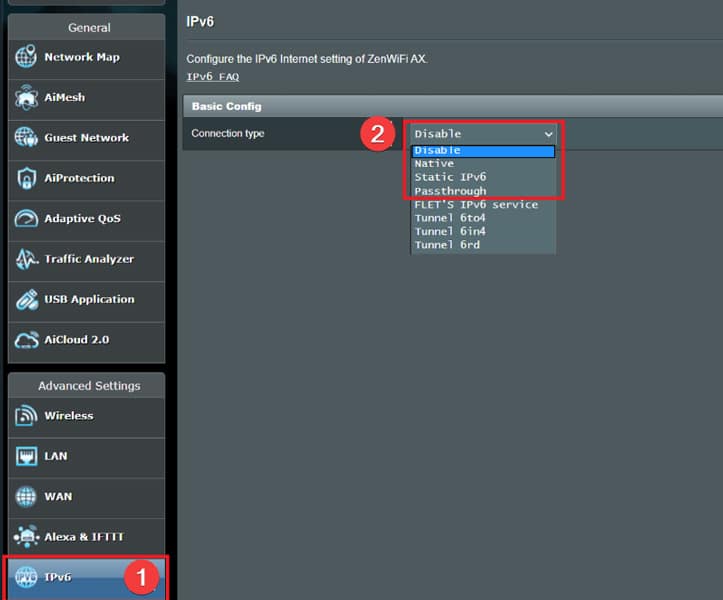
- ASUS: Go to the router’s Admin page, select Advanced Settings, then IPv6. Choose the Native option.
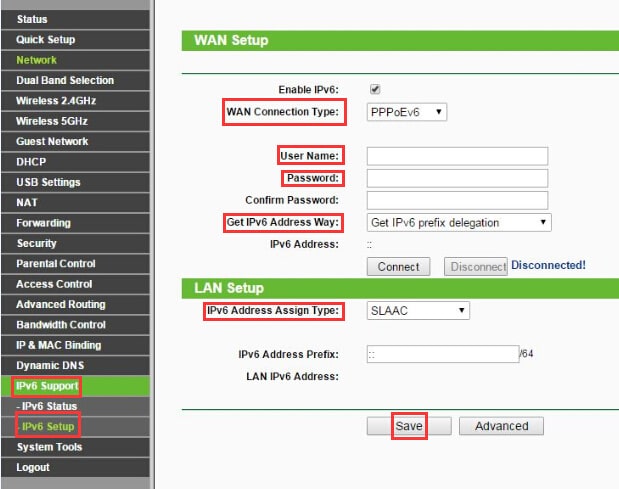
- TP-Link: First, go to the router’s login page and enter the credentials. After that, choose IPv6 Support. Enable and select the ISP’s preferred type.
Remember to save changes and reboot the router after any adjustments.
4. Enabling IPv6 on Xbox
To enable IPv6 on your Xbox, the approach differs between the Xbox Series X and Xbox One due to their varying capabilities in handling network protocols. Follow these specific steps for each console:
Xbox Series X
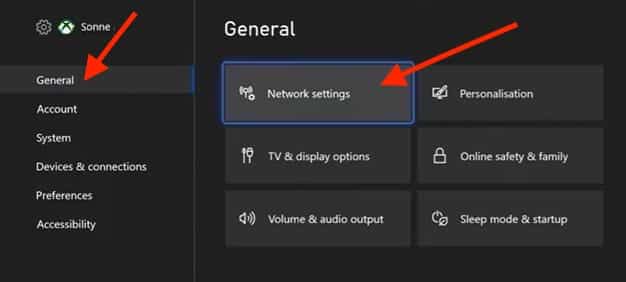
- Open the Xbox Settings, navigate to the main menu, and select Settings.
- Go to General > Network Settings and within the Settings menu.
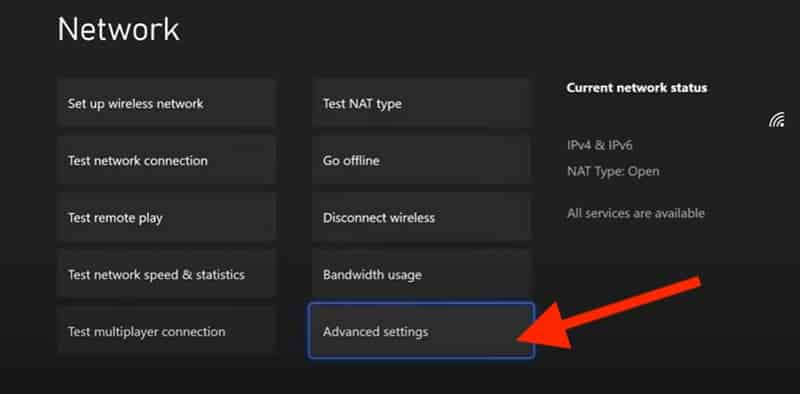
- In the Network menu, look for and choose Advanced Settings.
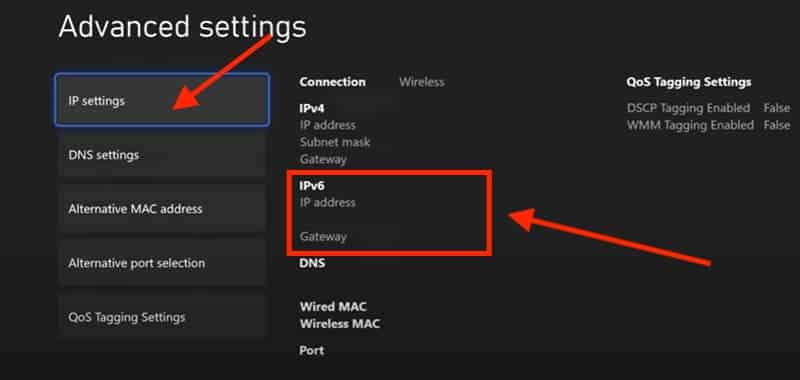
- Locate and select IP settings, then change from Automatic to Manual.
Xbox One
- Verify ISP Support: Confirm that your Internet Service Provider (ISP) supports IPv6.
- Check Router Compatibility: Ensure that your router is compatible with IPv6 and that IPv6 is enabled in its settings.
- Automatic IPv6 Usage: If IPv6 is available in your network setup, the Xbox One will automatically utilize an IPv6 connection.
5. Apply IPv6 DNS
DNS (Domain Name System) translates domain names into IP addresses. For IPv6, it’s important to use DNS servers that support the protocol. Common IPv6 DNS servers include Google DNS (2001:4860:4860::8888 and 2001:4860:4860::8844) and OpenDNS (2620:119:35::35 and 2620:119:53::53). Setting these in your router can improve browsing speed and reliability.
In the router settings, look for DNS server settings under IPv6 configuration. Input the preferred and alternate IPv6 DNS addresses and save your changes.
Verifying IPv6 Connectivity
Once you have configured your Xbox and router for IPv6, it’s crucial to test the connectivity. This can be done through several methods:
1. Xbox Network Test
- Use the built-in network testing feature on your Xbox.
- Press the Xbox button on your controller to open the guide.
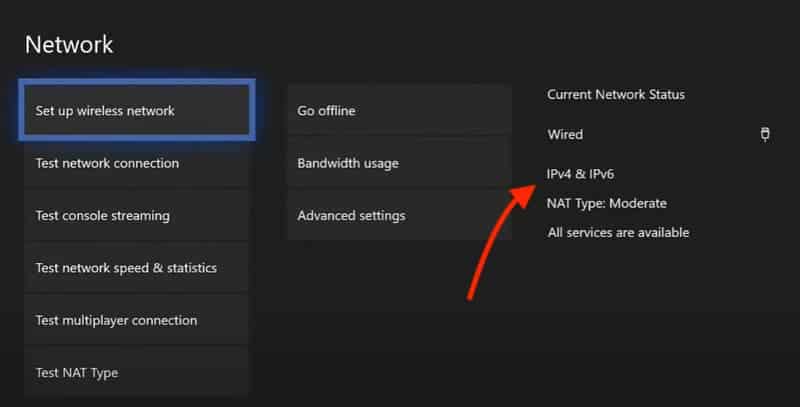
- Select Profile & system, then go to Settings and hit General.
- Finally, choose Network settings.
If your Xbox console has IPv6 connectivity, your Current Network Status will show as IPv4 & IPv6.
2. Online IPv6 Test Websites
You can use the Xbox’s web browser to visit IPv6 test websites like Test-ipv6.com. These sites can confirm if your console is successfully using an IPv6 connection.
3. Router Status Page
Check your router’s status page through its web interface. Most routers show the type of IP addresses assigned to connected devices, indicating whether your Xbox is on IPv6.
If the tests confirm IPv6 connectivity, your setup is successful. If not, check to see if the Xbox is still using IPv4. This could be due to the ISP not supporting IPv6 or an issue with the router configuration. In case of an incomplete setup or connectivity issues, revisit the previous steps or consult the troubleshooting section.
Common Issues and Solutions
Below, we have listed the two most common Xbox IPv6 issues and their solutions.
1. Xbox IPv6 Not Detected
If IPv6 is not detected, ensure your ISP supports it and that IPv6 is enabled on your router. Restarting your Xbox and router can also help refresh the network settings.
2. Xbox Intermittent Connectivity
If you experience intermittent IPv6 connectivity, it may be a signal strength issue. Try moving your Xbox closer to the router or using a wired connection.
3. Issues with Enabling IPv6 Feature
If your router and ISP support IPv6 but you can’t enable the feature, follow the steps below:
- Restart Network Devices: Restarting your Xbox and router can resolve connectivity issues.
- Update Firmware: Ensure both your Xbox and router are up-to-date.
- Manual IP Configuration: If needed, manually configure IP settings, particularly for Xbox Series X.
- DNS Settings: Using an IPv6-compatible DNS server may be necessary.
4. Contact Customer Support
If we’re unlucky in fixing the Xbox IPv6, your last resort is to contact your ISP or Xbox support, but make sure to:
- Document Your Steps: Note all the steps you’ve taken to set up IPv6.
- Error Messages: Report any specific error messages you encountered.
- Equipment Details: Have details about your Xbox model and router on hand.
Maximizing Gaming Performance
To maximize gaming performance on your Xbox, you should take care of your network connection and Xbox performance settings.
1. Network Related Configurations
To optimize your network for Xbox gaming with IPv6 :
- QoS Settings: If your router has Quality of Service (QoS) settings, prioritize your Xbox to ensure it gets sufficient bandwidth for gaming.
- Wired Connection: Use a wired Ethernet connection for a more stable and faster connection than Wi-Fi.
- Avoid Network Congestion: Try to reduce network traffic from other devices during gaming sessions.
2. Xbox Performance Settings
On your Xbox:
- Update Console: Keep your Xbox updated for the best performance.
- Close Unused Apps: Ensure no background apps are consuming network resources.
- Monitor Network Performance: Regularly check your network performance in the Xbox settings and adjust as needed.
Conclusion
Adopting IPv6 is more than just a technical evolution; it’s a necessary step towards future-proofing our increasingly interconnected world. For gaming, specifically for Xbox users, the transition to IPv6 is a leap towards a more robust, efficient, and seamless online experience. As the gaming industry continues to push the boundaries with online multiplayer games, cloud gaming, and other bandwidth-intensive services, IPv6’s vast address space and improved routing efficiency become indispensable. This transition also aligns with the growing trend of IoT devices in our homes, where each device requires its IP address.
Want to enable IPv6 on your Xbox?
Enhance your gaming experience with RapidSeedbox’s reliable IPv6 services. Enjoy faster connections, reduced lag, and exceptional support for seamless Xbox gaming.
Embracing IPv6 might seem daunting at first, given its technical nature, but the long-term benefits it brings to your gaming experience are undeniable. Improved connection stability, reduced latency, and enhanced security are just the beginning. As more ISPs, game developers, and console manufacturers continue to support IPv6, those who have made the early switch will find themselves ahead of the curve. Therefore, I encourage Xbox gamers to take this step not only to enhance their gaming experience but also to be ready for the exciting developments the future holds in online gaming.
0Comments