In this article, we will examine the global IPv6 adoption trends. Using maps from Google and APNIC, we will highlight varying IPv6 deployment levels worldwide, indicating modern internet infrastructure in some regions and challenges in areas with lower adoption. Furthermore, we also discuss potential growth opportunities, regional variations in tech development, and the implications for future technological leadership and internet connectivity.

Table of Contents.
- Adoption Trends: Maps and Analysis
- Room for Growth and Hidden Opportunities
- Who’s Leading in IPv6 Adoption?
- The Global IPv6 Adoption with DNS
- Web Prefers Native IPv6
- IPv6 Adoption: Predictions and Trends
- Conclusions.
1. Adoption Trends: Maps and Analysis.
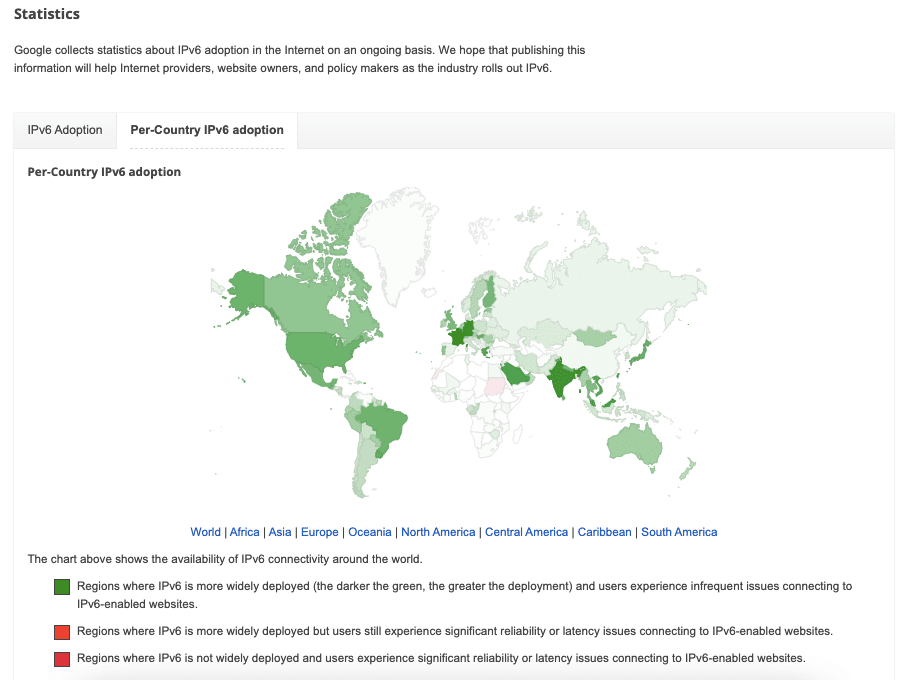
The following image from the same source (Google IPv6 Statistics) represents a world map illustrating the per-country adoption of IPv6. The map uses different shades of green to indicate the level of IPv6 deployment in each country:
- Dark Green: Represents regions where IPv6 is more widely deployed. In these areas, the deployment of IPv6 is significant, and users experience less issues when connecting to IPv6 websites.
- Light Green: Indicates the regions where IPv6 is also widely deployed, but users might still face reliability or latency iproblems when accessing IPv6 websites.
- Grey: Represents the regions where IPv6 is not widely deployed and users experience significant reliability or latency issues with IPv6 websites.
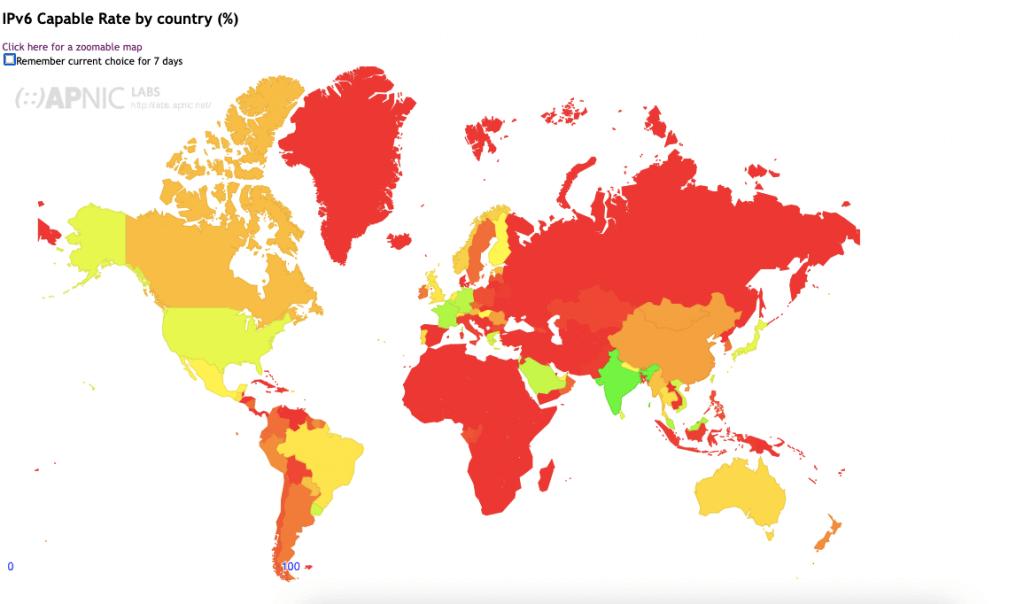
Another useful map for looking at these adoptions is directly from APNIC. The following Worldwide IPv6 Adoption statistics by APNIC show different colors but more or less correlate with the data from Google.
- Green, Yellow to Light Orange Colors. Countries with high IPv6 adoption rates have modern internet infrastructure and have widely implemented IPv6. The leaders are clearly India, France, and Germany.
- Dark Orange to Red. Countries with moderate to low IPv6 adoption rates face economic constraints, lack of expertise, or need regulatory incentives.
By looking at these maps, you might infer that certain regions have more advanced internet infrastructure and possibly a greater push towards modernizing their network capabilities. In contrast, other regions may have infrastructure that is lagging in adopting IPv6 technology.
It is obvious that regions such as North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, are leading in the adoption, indicating regional investments in network infrastructure and technology. Whereas, other regions show minimal to no IPv6 adoption. These regions may be facing significant challenges, such as lack of infrastructure, regulatory hurdles, or prioritization of other technological investments.
Room for Growth and Hidden Opportunities.
These maps indicate where there is room for growth in IPv6 deployment. They suggest opportunities for investment and development in Internet technologies. If certain countries are making rapid progress while others are stagnant, this may predict where future internet growth and innovation will be concentrated. Additionally, such maps can inform policymakers where efforts and resources may be needed to improve IPv6 adoption and could guide international cooperation on internet technology standards.
Who can benefit from such IPv6 adoption maps?
These visual representations of global IPv6 deployment, are helpful for internet providers, website owners, and policymakers for learning about the current state of IPv6 adoption. The goal is to support these stakeholders in making decisions that will facilitate the industry’s transition to IPv6.
Who’s Leading?
From the previously presented maps, it can be inferred that countries like India, Vietnam, Taiwan, Malaysia, Saudi Arabia, Greece, France, Germany, and Belgium are leaders in IPv6 adoption (specifically for IPv6-enabled Users collected from Google).
From another source of data: Eric Vyncke’s Daily IPv6 Statistics regarding IPv6 adoption (for all adoption vectors, including Web, Email, DNS) it can be seen that Belgium leads with a 74.93% adoption rate for Web among the top 50 domains, with the United States at 70.02%.
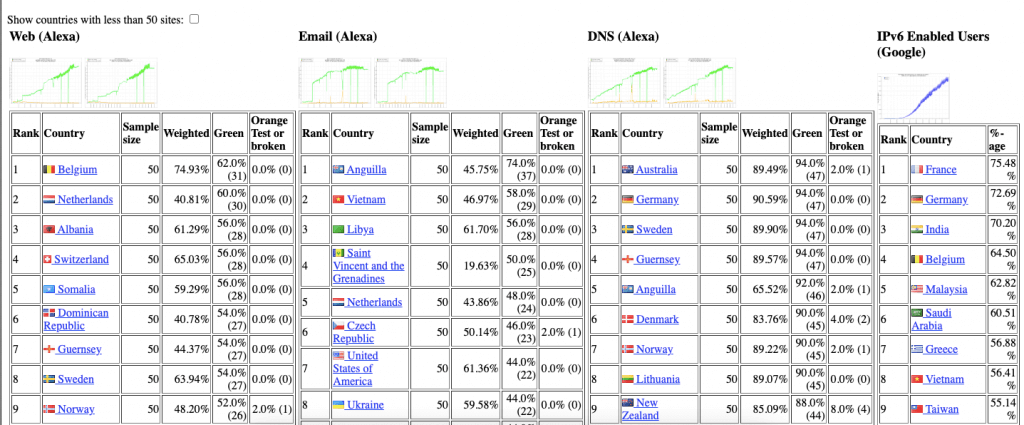
The measure considers successful HTTP connections over IPv6 (green) and whether a domain has an IPv6 address (orange for indirect success, red for unavailability). The stats also highlight DNS and email readiness for IPv6, where Australia and Germany show high readiness above 89%.
Such data visualizations indicate growing support for IPv6, which is crucial for the internet’s future scalability.
2. The Global IPv6 Adoption with DNS.
IPv6 has seen a gradual increase in adoption over the last decade, with current usage between 30 to 40%. Despite the vast address space of IPv6 addressing the limitations of IPv4, the transition has been slow due to compatibility issues requiring devices to support both protocols (see, IPv6 transition mechanisms).
In a Cloudflare report “Using DNS to estimate the worldwide state of IPv6 adoption (December 2023 by Carlos Rodrigues)” they found that IPv6 traffic accounted for approximately 36% of all internet traffic by the end of October 2023, with variations when accounting for bots and human users. However, true IPv6 adoption requires both client and server capabilities. Such DNS data indicates that while 30.5% of DNS queries are for IPv6, only 43.3% of servers are IPv6-capable, suggesting that actual usage is lower.
The disparity highlights the need for increased IPv6 deployment by ISPs and content providers. Cloudflare’s initiatives, like free IPv6 support and DNS64 services, are steps toward facilitating this transition, aiming for a future where the internet is no longer constrained by IPv4 limitations.
3. Web Prefers Native IPv6.
The following image collected from Google IPv6 Statistics depicts a line graph representing the IPv6 adoption rate over time. This adoption of IPv6 is specific among Google users. The data collected by Google, starts from around 2010 and extends up to date. The percentage of users accessing Google via IPv6 has increased significantly over the years, reaching 41.23% by January 15, 2024.
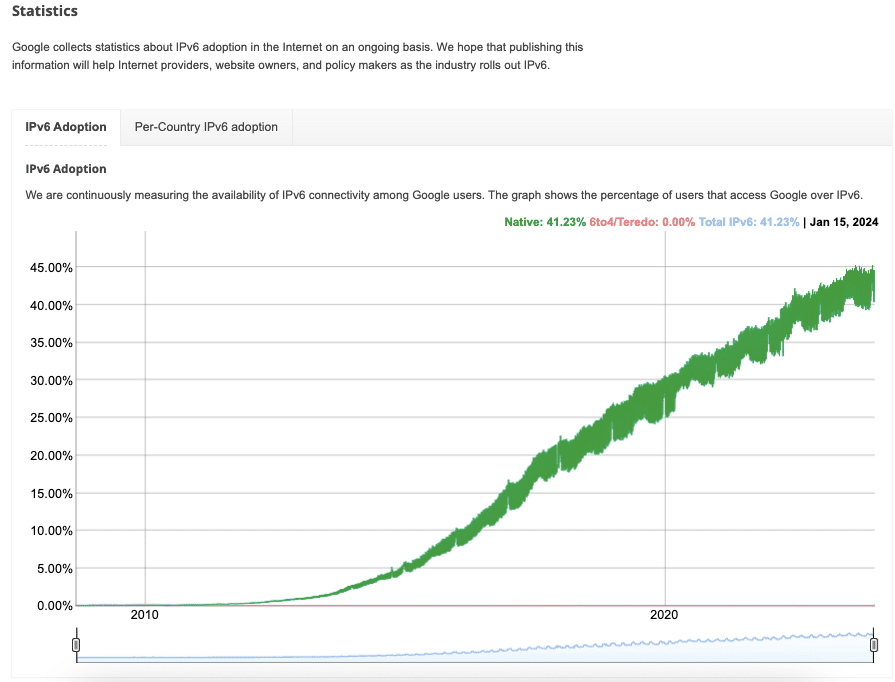
The trend line shows a consistent upward trajectory, illustrating that the adoption of IPv6 has been growing steadily. The graph demonstrates the increasing prevalence of IPv6, suggesting that more devices and internet services are transitioning to use the newer internet protocol.
The graph shows two terms Native and 6to4/Teredo. The term “Native” refers to users who are directly accessing Google over IPv6, not using transitional technologies like 6to4 or Teredo, which are indicated to be at 0.00%. This suggests that the reported 41.23% of traffic is purely through native IPv6 connections.
4. IPv6 Adoption: Predictions and Trends.
The predictions and trends for IPv6 adoption (based on the data provided by major global companies like Google or CloudFlare), can be rounded as follows:
Note: The following points are stipulations based on the previous data visualizations. They do not intend to predict the future adoption on IPv6.
a. Steady Growth of IPv6 Adoption
Graphs shows a consistent upward trend, so we can predict that IPv6 adoption will continue to grow as the limitations of IPv4 become more pronounced and the benefits of IPv6 become widely recognized.
b. Regional Variations in Adoption
The maps showing per-country adoption indicate that a few regions (indicating higher adoption rates) are likely ahead in terms of modernizing their internet infrastructure. These regions may offer better connectivity and network performance.
c. Correlation with Technological Development
Regions with higher IPv6 adoption may also be those with more advanced technological infrastructure overall. This could correlate with higher levels of digital transformation in businesses and government services.
d. Predicting Future Leaders in Tech
Countries leading in IPv6 adoption might be the ones setting standards for future internet technologies and could dominate in sectors like cloud computing, IoT (see IoT and IPv6), and other services that require a large number of IP addresses.
e. Potential for Increased Adoption
Other areas may have growth potential. As IPv6 benefits become more apparent, these regions might see a surge in adoption rates, especially as newer technologies that rely on IPv6 become mainstream.
f. Latency and Connectivity
If the statistics show that regions with higher IPv6 adoption experience fewer connectivity or latency issues, it might indicate that transitioning to IPv6 can offer a more reliable and faster internet experience.
g. Security Implications
With the new security features inherent in IPv6, regions that adopt it might experience a shift in their cybersecurity landscape, potentially reducing certain types of network-based threats.
h. Implications for Content Providers
As IPv6 becomes more prevalent, content providers and services will likely need to ensure they are accessible over both IPv4 and IPv6 to maintain their reach and performance standards.
Conclusions.
The data provided by reports and analysis from major companies (including Google, APNIC, and Cloudflare) suggest a steady increase in its implementation worldwide. Countries like Belgium, India, France and the United States are leading, with adoption rates above 70% in certain sectors, indicating a shift towards more widespread IPv6 utilization.
As IPv4 address exhaustion becomes more pronounced, it’s expected that more countries and companies will transition to IPv6 for its larger address space and improved network efficiency.
0Comments