Want a quick answer? — Is Tor Safe? Yes.
But still, we believe you shouldn’t fall for a quick “yes/no answer” to “Is Tor Browser safe?”. After all, there are many different use cases, requirements, resources, etc. So, whether Tor Browser is safe or not is all about you, what you are doing with it, how safe you can use it, and what you can avoid while using it.
So, let’s dive deeper into this Tor Browser guide and understand how safe it is and how to make this fantastic browser the safest.

In this guide, we’ll explore the privacy and security features of the Tor Browser. We’ll cover the basics of how Tor works, its risks and benefits, and how to enhance your security when using it. We will also compare it to VPNs and other privacy tools.
Table of Contents.
- What is Tor, and How it works?
- How does Tor make the TOR Browser safe?
- The Potential Risks of Using Tor.
- How to use Tor Browser safely?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Words.
1. What is Tor Browser, and How it works?
The Tor Browser is a web browser like Chrome or Firefox explicitly designed to access the Tor network.
TOR (The Onion Router) is an open-source project that allows anonymous and secure internet browsing. It uses a very efficient mechanism that encrypts and routes internet traffic through a decentralized network of relays (also known as the Tor network). When your internet traffic gets routed and encrypted through this network of multiple random nodes before, it becomes extremely difficult for anyone to trace it back to you. So, technically, no one can track your online activity and location using the TOR network.
The Tor Browser is based on the Firefox web browser and comes built-in with the necessary settings and plugins to work with the Tor network. When users access the internet using the Tor browser, their traffic gets automatically routed through the Tor network.
What Happens When You Use Tor Browser?
To learn whether the Tor Browser is safe, it is vital to understand its backend technology. The Tor Browser is explicitly designed to access this decentralized network of relays (The Tor Network), allowing automatically full internet anonymity. When you open your Tor Browser, it automatically connects to this network.
To explain how things happen, refer to the flow and each diagram below.
a. Connection Setup (1)
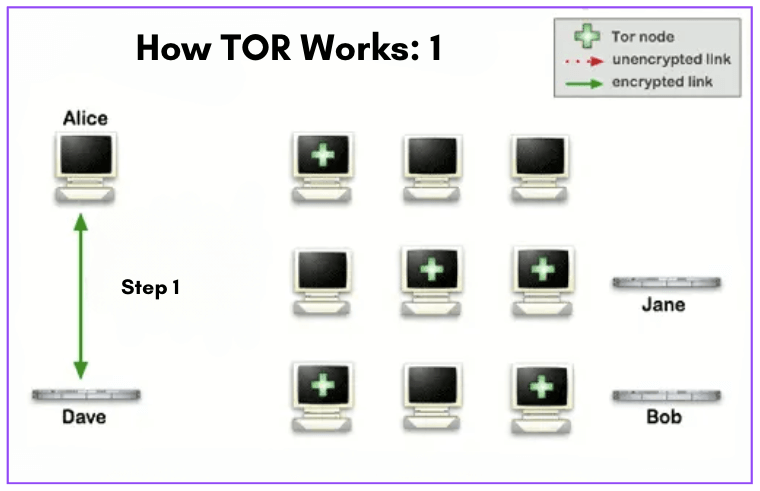
Refer to the network diagram below (How Tor Works: 1).
- When Alice opens her Tor Browser, it contacts a central server (i.e., Dave) called a Directory Authority to obtain a list of the relays working in the Tor network. This list contains information about each relay, including its IP address, bandwidth capacity, and public key. Alice’s Tor Browser uses this list to establish a connection to the network.
- In the diagram, you’ll also see a network of nodes (Tor Network). The ones with a green cross are the Tor nodes which were chosen randomly as the path progressed toward its destination.
b. Connection Phase (2).
Refer to the network diagram below (How Tor Works: 2).
- Alice opens her Tor browser and sends a request to access a website (Bob) just like she would for Chrome or Brave. Alice’s Tor Browser will connect to Bob through the Tor network.
- The browser sends a request (Step 2). It gets immediately encrypted and sent to the first node in the Tor network, called the entry node. It decrypts the request and forwards it to the next node in the network, which is selected randomly.
- The next node encrypts the request again and forwards it to another randomly selected node. This process continues many times until the packet request reaches the exit node. The exit node decrypts the request and sends it to the website (Bob).
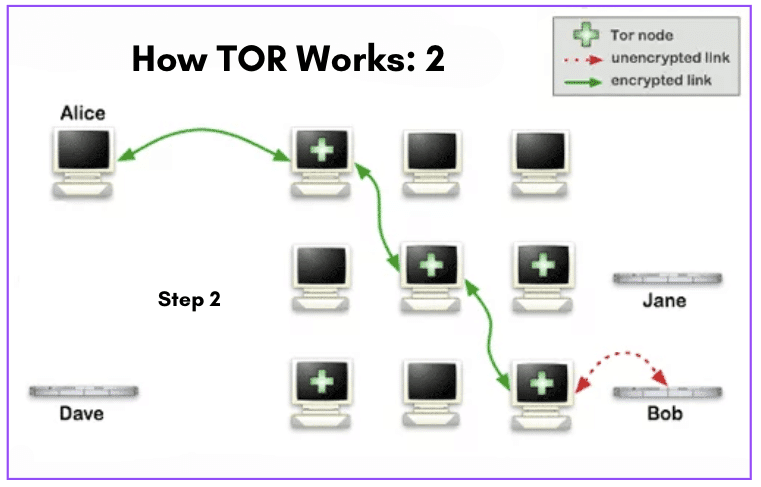
- The website (Bob) sends back the requested information, which is encrypted and sent back through the network with a similar path.
Alice’s (Tor Browser’s) IP address is only used initially. So it remains out of sight throughout the whole process, making it almost impossible for a middleman to trace back the online activity or location.
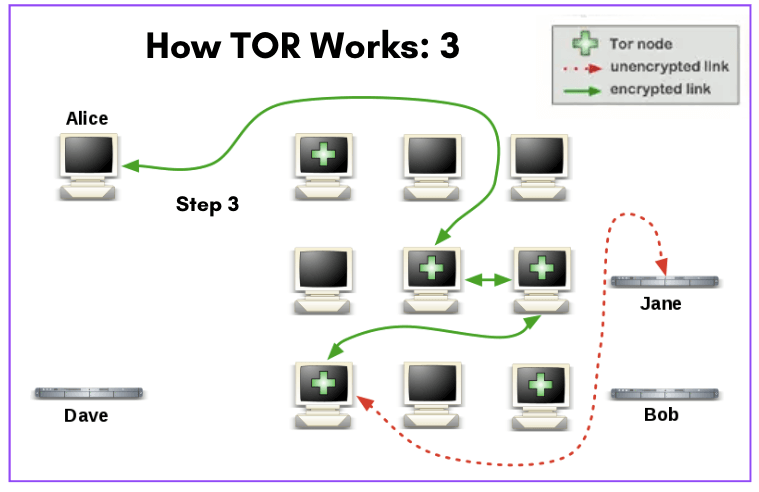
c. New or Connection Timeout (3).
Refer to the network diagram below (How Tor Works: 3).
- If the user (Alice) later wants to visit another site or there is a connection timeout, her Tor Browser will select a second random path (completely unrelated to her previous traffic’s path).
- Like the previous scheme, the green links are encrypted traffic, while the red links are unencrypted. But you will notice that the path is completely new.
2. How does Tor make the TOR Browser safe?
If you followed through the previous chapter, you might now know how Tor protects your traffic. How it routes, encrypts, and randomizes each path toward its destination.
It is ‘nearly’ impossible to attempt to trace back the origin of Tor Browser-generated traffic. This is precisely the idea behind the Tor network design.
Note: We introduce the word ‘nearly’ in the previous statement because, except for an air-gapped system, no system generating traffic across a public network is immune to being traced back. Someone with extremely significant resources, capabilities, and motivation may still be capable of correlating several factors and potentially tracing back to the path, such as > Tor client < Entry Node < X < X < … < X < Exit Node < Website.
a. Tor makes traceback attempts extremely challenging; here is why.
- Multiple layers of encryption: Tor uses a concept known as multiple layers of encryption or Onion Routing. In this process, each relay in the Tor network only knows the previous and next relay in the path. This type of encryption makes it extremely challenging for someone to decipher the complete traffic path.
- Randomized routing: As you might already know (from the previous chapter), the network uses random paths for each connection. It selects (every time) different relays for different users and sessions. This randomness complicates Tor path traceback attempts even more.
- No centralized logs: Tor is a decentralized network composed of thousands of user-volunteered nodes. So there are no centralized logs of your activity or connection details. This further minimizes the ability to trace traffic back traffic to its source.
b. Here are a few of Tor Browser’s security and privacy features.
Besides being backed by the aforementioned features, including multiple layers of encryption, randomized routing, and no centralized logs, the Tor browser also comes with a few additional privacy features under its sleeve.
Auto-connect to Tor Network.
- Once you start with Tor, you’ll be immediately requested to connect to Tor. You can also configure the connection, including setting up bridges (a feature to let you use the Tor network wherever it is blocked) or the use of an anonymous proxy (to add an extra layer of anonymity)
- Once you successfully connect, you’ll see the Internet icon “online” and the “Tor Network” also online.
The Privacy & Security settings in the Tor Browser.
- The Tor Browser has a handful of useful features to improve your online privacy and security. Go to Tor Browser > Preferences > Privacy & Security to access them.
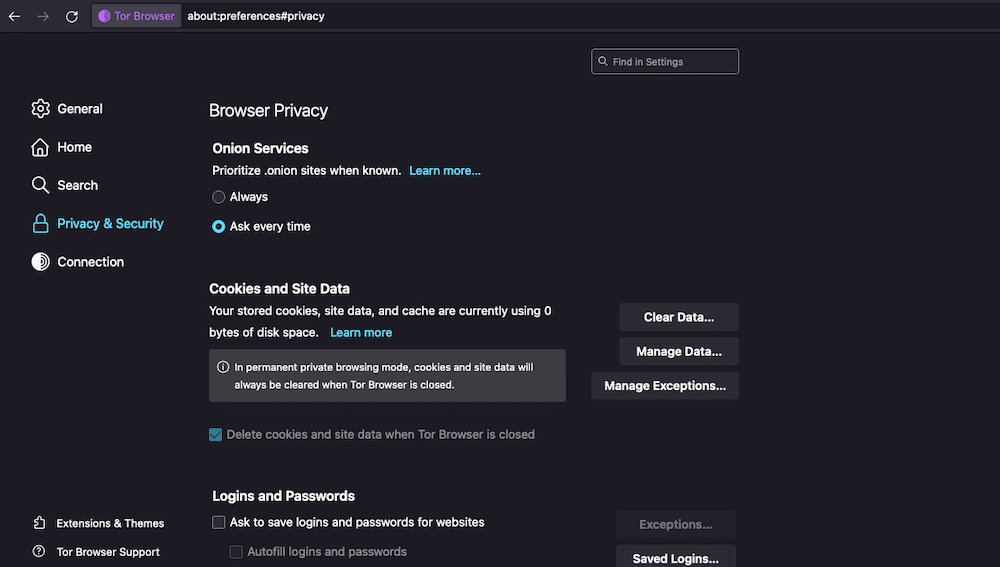
Here is a brief description of each of these features:
- Browser Privacy: This setting allows you to set priorities for onion sites, automatically clear cookies and site data, and manage your login/passwords.
- Onion Services Authentication: A setting that allows you to manage saved keys for accessing onion services.
- History: Just like any good browser, Tor Browser also allows you to configure how it remembers browsing, downloads, forms, and search history.
- Address Bar: Customize suggestions from browsing history, bookmarks, open tabs, shortcuts, and search engines.
- Permissions: Manage permissions for location, camera, microphone, notifications, autoplay, and VR. Also, block pop-up windows and warn about installing add-ons.
- Security: Choose from predefined security levels. Also, configure Tor Browser to block harmful and deceptive content and dangerous downloads and warn about unwanted software. Tor Browser also allows you to manage certificates and enforce HTTPS encryption.
The above settings will provide the control you need to improve the Tor Browser’s privacy, security, and browsing behavior. So you can use Tor Browser safer and customize your experience based on your preferences.
c. A default search engine with the best privacy.
Tor Browser comes with privacy-focused Duck Duck Go as its default search engine. Unlike traditional search engines like Google or Bing, DuckDuckGo does not store or track your information, search history, or personally identifiable data.
DuckDuckGo allows you to search without being tracked (as most popular search engines do), with full site encryption and full incognito all the time.

Obviously, you can use this search engine (DuckDuckGo) with any web browser, and you can also use Tor Browser with Google, Bing, or other search engines.
3. The Potential Risks of Using Tor.
Although Tor Browser is safe as its features and underlying mechanism anonymize your communications over the Internet, it also allows you to browse websites hosted on hidden services — or infamously known as the Dark Web. Tor allows you to access these publicly unavailable services and websites unindexed by popular search engines known as .onion addresses. And unfortunately, most of the time, these unpopular sites come with lots of potential risks.
Note: Tor browser is one of the “safe gateways” to the dark web (a small part of the deep web, not indexed by search engines). Although not everything happening around the dark web is entirely “bad,” and the bad things that exist in the dark web have been overly exaggerated, we recommend not visiting the dark web.
So, although Tor Browser is safe, that level of safety would depend on how you use it. Below are four significant risks that you should consider while using Tor.
a. Four significant risks to consider while using Tor.
- Law enforcement and government monitor the dark web. While the government knows about privacy rights, certain laws empower them to gather intelligence, track down criminals, and disrupt their operations. Law enforcement and governments are actively monitoring the dark web to fight against drug trafficking, cybercrime, weapon sales, identity theft, and more illegal activities.
- While navigating the dark web, risks and negative experiences exist. Albeit this rarely happens, the dark web is a gateway to risks and negative experiences, including ‘unintentional’ exposure to disturbing content, engaging in illegal activities, and identifying theft and cybercrime. Although not recommended — if you go through the dark web, exercise extreme caution due to the unregulated nature of the platform and the potential legal consequences.
- The dark web is a breeding ground for hackers, malware, and illicit activities. The dark web houses hackers, malicious files, malware, and more. It is like the dark alleys of a gigantic city. The design of Tor attracts malicious actors who exploit this anonymity. It allows them to host thousands of hacking forums and malware distribution channels, trade illegal goods, and even involve in cybercriminal operations. If you frequent the dark web, you can unintentionally become exposed to illegal activities.
- Lots of websites and search engines restrict Tor browser users. Although this is not really an online or privacy risk, it limits your browsing experience. Some websites and online services actively block Tor users from accessing their content. These sites see ToR as a security threat and will find ways to block them. They perceive ToR’s anonymous users as a security risk because they can’t track them.
4. How to use Tor Browser safely?
Although ToR provides anonymity, there is never a 100% guarantee of complete protection against third-party (government and intelligence agencies) surveillance. In some countries, intelligence agencies and law enforcement use the most sophisticated technology to monitor Tor traffic. And in some cases, they are successful!
Note: We recommend avoiding the dark web— you may unintentionally fall prey to identity theft or impersonation! Dark web websites use “.onion” domains instead of the typical “.com” or “.net” domains. So, if you encounter a website with a “.onion” domain, it is likely hosted on the dark web. Do not engage with that website. Below is an example of a .onion link.
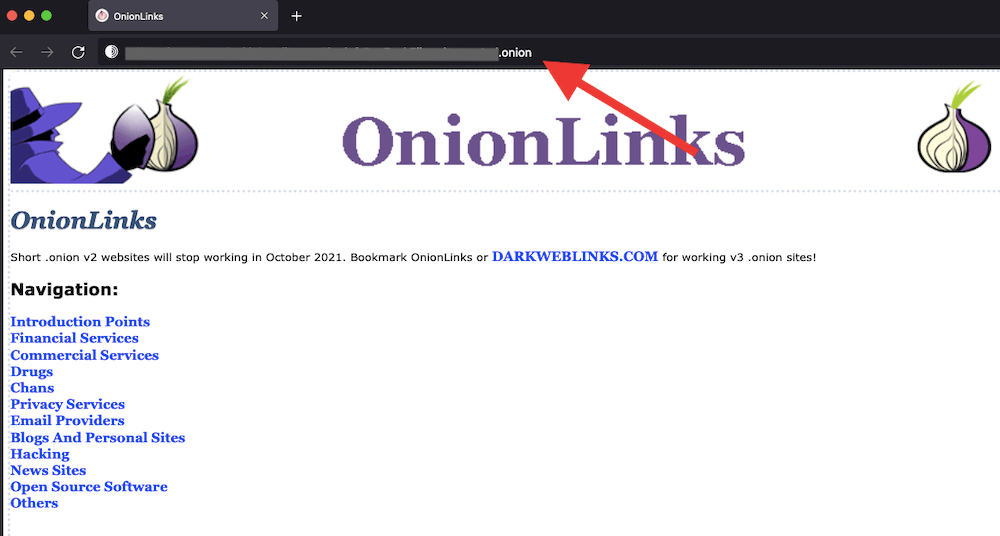
a. How to use Tor Browser safely?
- Do not trust HTTP sites; stick to HTTPS. Every modern web browser (including Tor Browser) can automatically redirect (or reject) any HTTP webpage. These types of webpage protocols are not encrypted. While using the Tor browser, ensure the HTTPS padlock is always on.
- Exercise extreme caution when downloading files from the Tor network. The best advice here is to use your common sense. Stick to reputable and known sources (avoid .onion domains at all costs). Also, use reliable and updated antivirus software and avoid executing any suspicious files.
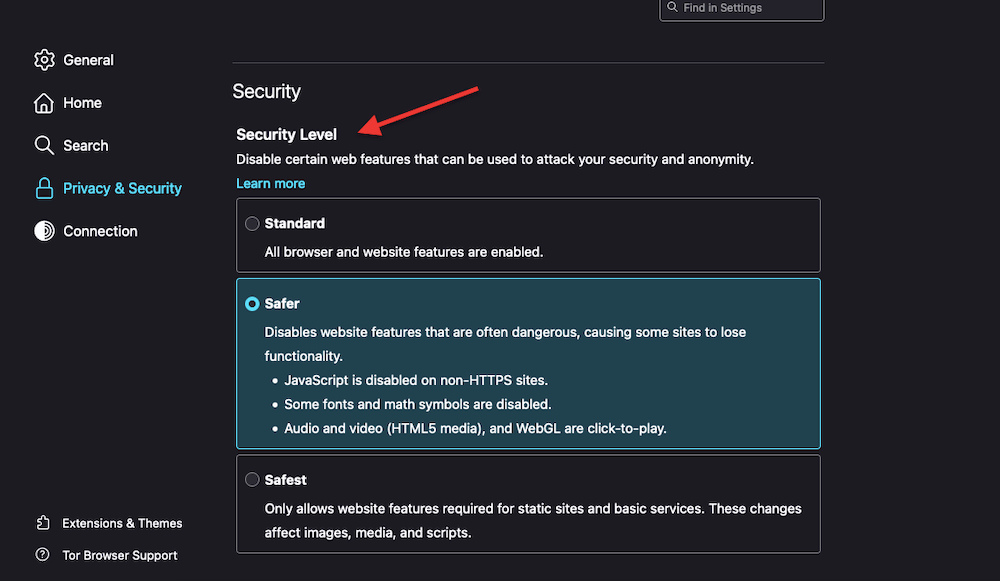
- Also, don’t forget to play around with ToR’s security filters. Go to Preferences > Privacy & Security > Security > Security Level > Choose between Standard, Safer, and Safest.
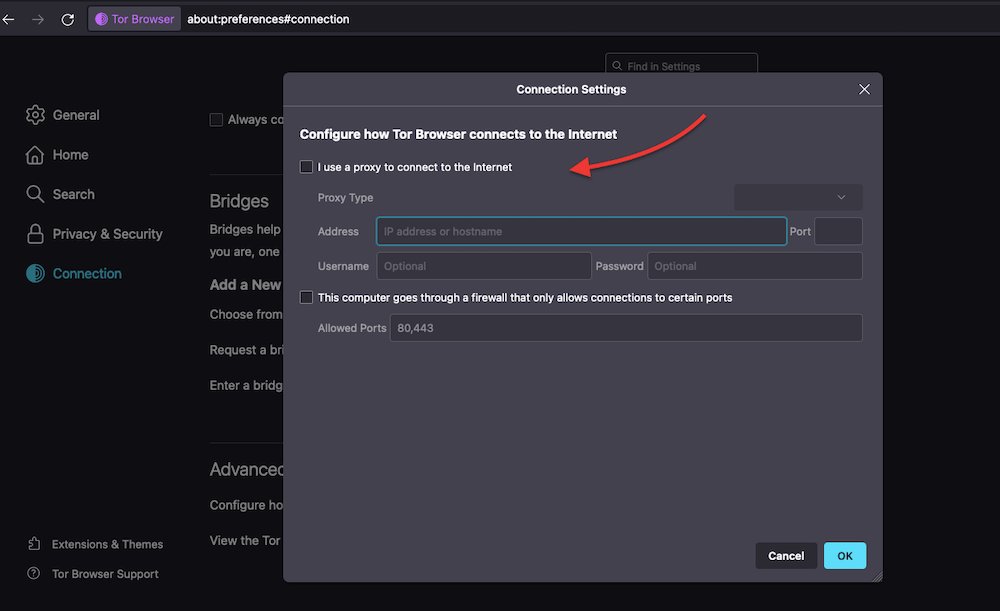
- Use ToR in combination with VPN or Proxy. Always remember that using a VPN or proxy over Tor may slow down performance. It also introduces a new “traffic hop” that receives your traffic with the capabilities to track and store your internet browsing logs. Learn more about this in VPNs vs. Proxies: Six differences.
- But still, modern and reputable VPN and proxy providers will help add another privacy layer (encryption in the case of VPNs and IP masking for Proxies) to your Tor traffic. Never use a free VPN or proxy service provider; always use no-logs policy VPNs and fully anonymous SOCKS5 proxies.
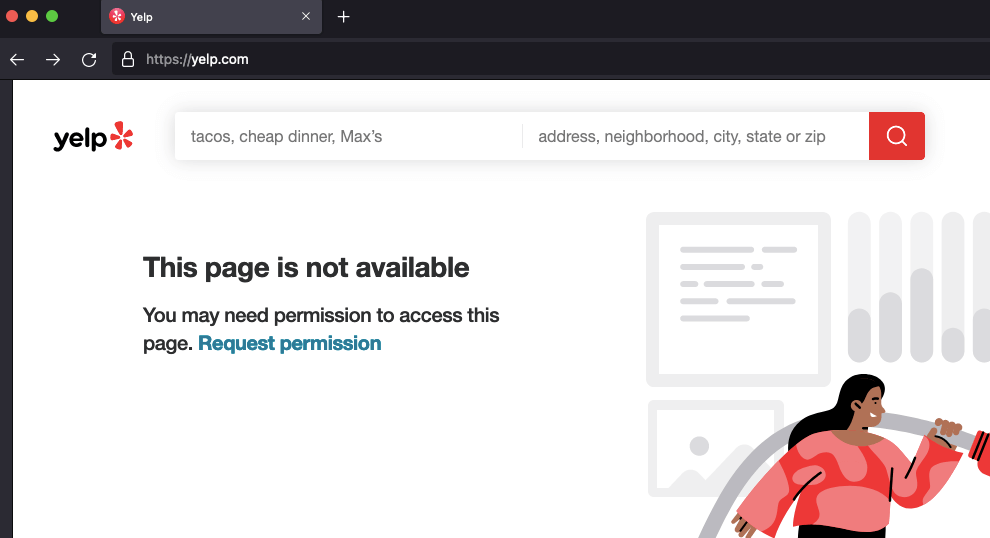
- Respect a website that doesn’t grant you access as a ToR user. Although you could use a Tor bridge (as described above) to bypass any restrictions on accessing content, it is generally not recommended. It is better to follow the rules and respect a website’s terms of service and legal restrictions.
5. Is Tor Browser Safe?: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ).
a. Tor vs. VPNs: What are their differences?
Although Tor and VPNs are both tools that aim to improve online privacy and security, they do have fundamental differences. As you might already know, Tor uses a network that anonymizes your internet traffic. Tor provides strong anonymity but can be slower and may not encrypt all traffic. VPNs, on the other hand, create a secure and encrypted tunnel between your device and the VPN server, protecting your traffic from potential eavesdroppers. They offer encryption, faster speeds, and the ability to choose server locations but leave you to fully rely on trust in the VPN provider.
b. Is Tor illegal to use?
No, Tor is not illegal to use. It is a legitimate software designed to protect online privacy and anonymity. Its use is encouraged between journalists, activists, researchers, and everyday users, who want to protect their identity from surveillance or censorship. Tor is not illegal in the United States, Canada, European Union, or Australia, but it is heavily restricted in China, Russia, and Venezuela. Although it could be used for lawful and unlawful actions, the software itself is not illegal. The improper use of this tool is what becomes a problem for the law.
d. How to use Tor Browser to access region-specific content?
If you want to bypass geo-restrictions or access region-specific content with Tor Browser, you can set a specific exit node (based on country) on Tor Browser. Follow these steps:
- Find Tor Browser’s installation folder on your computer. Navigate to the path: browser > Tor browser > Tor > data.
- Look for a file named “torrc” and open it using a text editor like Notepad. Scroll to the end of the document and create a new line.
- On the new line, type “ExitNodes {country code}” without the quotes.
- For example, to set the exit node to the United States, type: ExitNodes {US}.
- For China, type: ExitNodes {CN}.
- Save the changes to the “torrc” file.
- Restart Tor Browser for the new exit node configuration to take effect.
e. How to uninstall Tor Browser?
To uninstall this browser, follow the standard uninstallation procedure for your operating system. On Windows, you can go to the Control Panel > “Programs” or “Apps,” > find Tor Browser in the list > choose the option to uninstall it. For macOS, you can drag the Tor Browser application to the Trash bin. On Linux, you can use the package manager or manually delete the Tor Browser directory.
f. Why is Tor so slow?
Tor could be slow for many different reasons. The multi-layered encryption and traffic routing through multiple volunteer-operated nodes will undoubtedly introduce latency. The network’s limited bandwidth and the nodes’ potential congestion can also slow down speeds. Tor’s slow speed is the trade-off for its fantastic anonymity and privacy.
G. How to download torrents using Tor Browser?
Although you could use the Tor browser to download torrents via a web browser torrent client, it is generally not recommended (and goes against the rules of the Tor Network). The Tor network is primarily designed for anonymous web browsing, and its infrastructure will not be able to handle the bandwidth requirements of torrenting. Instead, we recommend using a seedbox to handle all torrent downloads, while you can still use Tor Browser for torrent browsing and downloading.
h. How to disable javascript in Tor?
Before disabling JavaScript in Tor, it is important to note that when you disable it, the functionality and appearance of some websites will also be affected. But if you value your privacy and anonymity over your user experience, disabling JavaScript in TorBrowser can be a smart move to improve your privacy. To disable JavaScript in Tor Browser, follow this instruction.
- Go into the Tor Browser’s URL bar and type “about:config”
- Accept the confirmation message
- In the search bar, type “javascript.enabled”
- Double-click on “True” to change it to “False”.
6. Final Words.
The Tor Browser is perfect for protecting your online privacy and anonymity. While the simple answer is “yes” to the question of whether Tor Browser is safe, it’s essential to consider the context of its usage and take necessary precautions.
You can improve its safety and security by understanding how Tor works and implementing best practices. Remember that there are potential risks. Always use trusted search engines, and follow guidelines for safe Tor usage.
As always, stay informed, stay vigilant, and enjoy the benefits of browsing with Tor.
0Comments